Evaluating the consistency of lenition measures: Neural networks' posterior probability, intensity velocity, and duration
Abstract
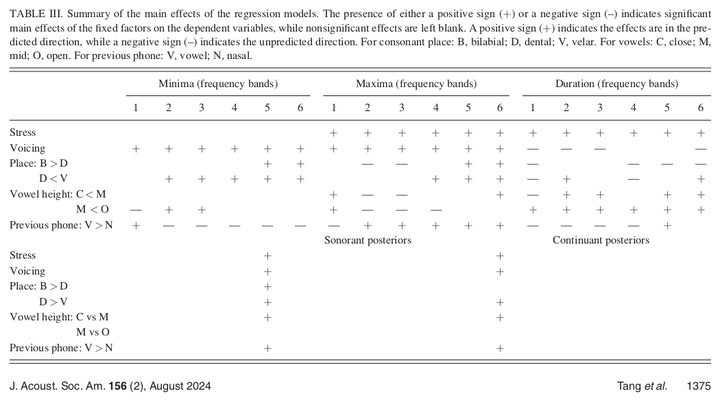
Predictions of gradient degree of lenition of voiceless and voiced stops in a corpus of Argentine Spanish are evaluated using three acoustic measures (minimum and maximum intensity velocity and duration) and two recurrent neural network (Phonet) measures (posterior probabilities of sonorant and continuant phonological features). While mixed and inconsistent predictions were obtained across the acoustic metrics, sonorant and continuant probability values were consistently in the direction predicted by known factors of a stop’s lenition with respect to its voicing, place of articulation, and surrounding contexts. The results suggest the effectiveness of Phonet as an additional or alternative method of lenition measurement. Furthermore, this study has enhanced the accessibility of Phonet by releasing the trained Spanish Phonet model used in this study and a pipeline with step-by-step instructions for training and inferencing new models.